
Foot Reflexology Chart Accurate Description Corresponding Stock Vector
The talus is held in place by the foot bones surrounding it and various ligaments. 4. Calcaneus. The calcaneus is more commonly known as the heel bone. It is the largest of the foot bones and has a quadrangular shape. The calcaneus is the most commonly fractured tarsal bone, usually from a high fall.

Foot organs map the body of the eye model human model anatomy
The foot is the region of the body distal to the leg that is involved in weight bearing and locomotion. It consists of 28 bones, which can be divided functionally into three groups, referred to as the tarsus, metatarsus and phalanges. The foot is not only complicated in terms of the number and structure of bones, but also in terms of its joints.

Anatomy Bones Learning Skeleton Feet Chapter 5 Appendicular Skeleton
Foot: Anatomy. The foot is the terminal portion of the lower limb, whose primary function is to bear weight and facilitate locomotion. The foot comprises 26 bones, including the tarsal bones, metatarsal bones, and phalanges. The bones of the foot form longitudinal and transverse arches and are supported by various muscles, ligaments, and.

image lateral_ankle for term side of card Ligament Tear, Ligaments And
Because they are so complicated, human feet can be especially prone to injury. Strains, sprains, tendonitis, torn ligaments, broken bones, fallen arches, bunions, corns, and plantar warts can all occur. Here we will talk more about the anatomy of the human foot and its many moving parts.

Foot body organ connection. Chinese medicine. Which part of the foot
Introduction A solid understanding of anatomy is essential to effectively diagnose and treat patients with foot and ankle problems. Anatomy is a road map. Most structures in the foot are fairly superficial and can be easily palpated. Anatomical structures (tendons, bones, joints, etc) tend to hurt exactly where they are injured or inflamed.
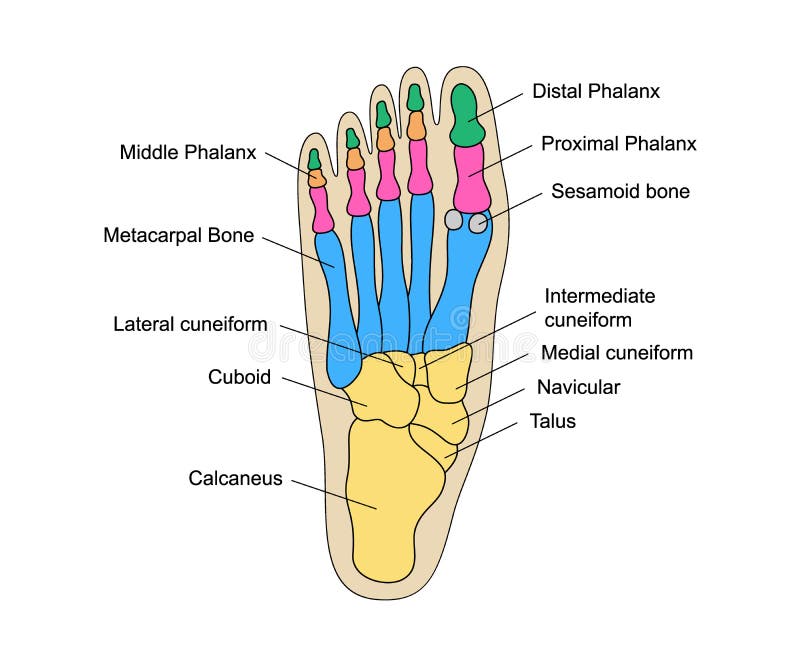
Human Foot Bones Anatomy with Descriptions. Educational Diagram of
Navicular Many of the muscles that affect larger foot movements are located in the lower leg. However, the foot itself is a web of muscles that can perform specific articulations that help.
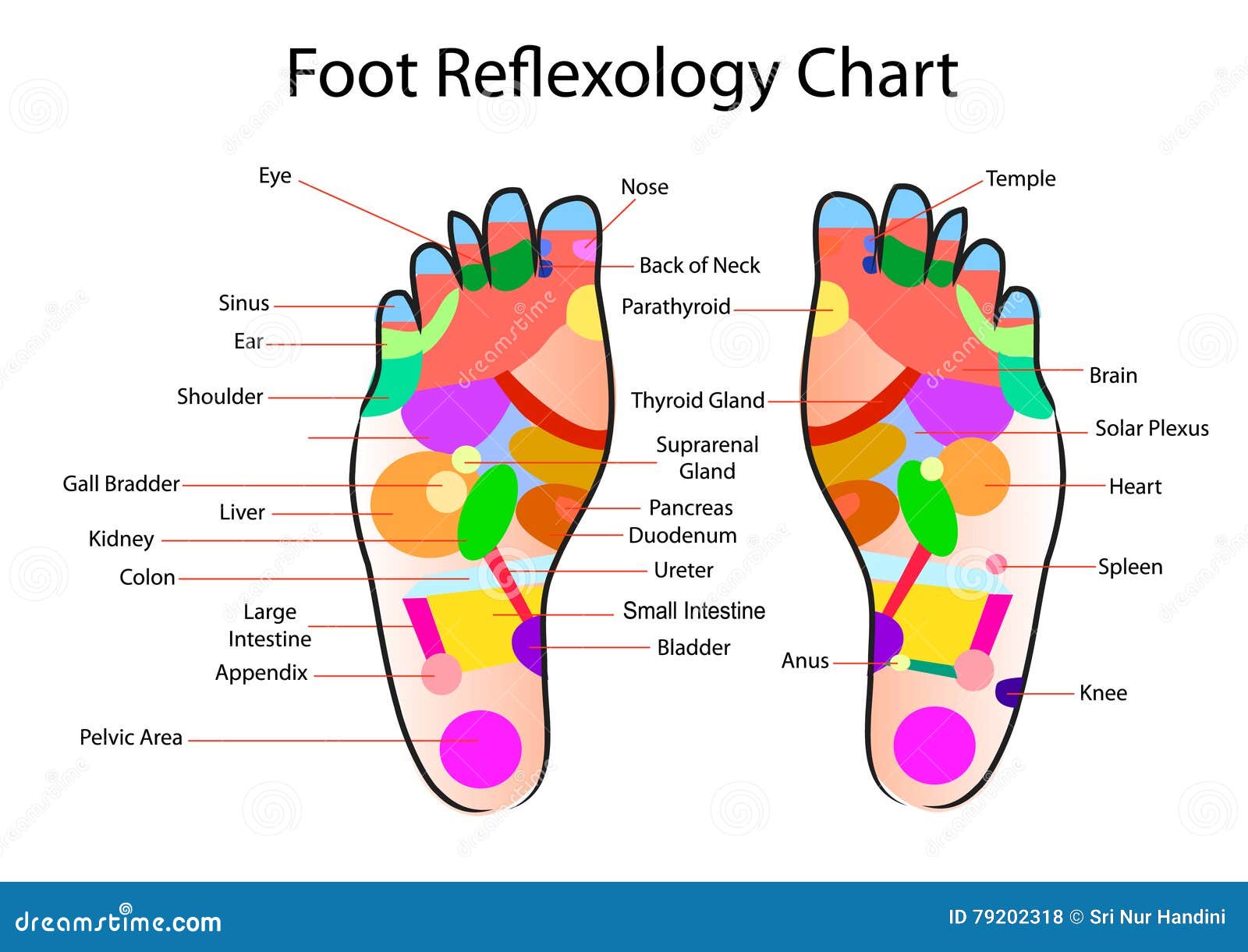
Foot reflexology chart stock vector. Illustration of accurate 79202318
The foot is a complex part of the body that is made up of many bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. It can easily be injured, develop diseases, or get infections. Bunions, claw toes, flat feet, hammertoes, heel spurs, mallet toes, metatarsalgia, Morton's neuroma, and plantar fasciitis are a few examples of foot problems.
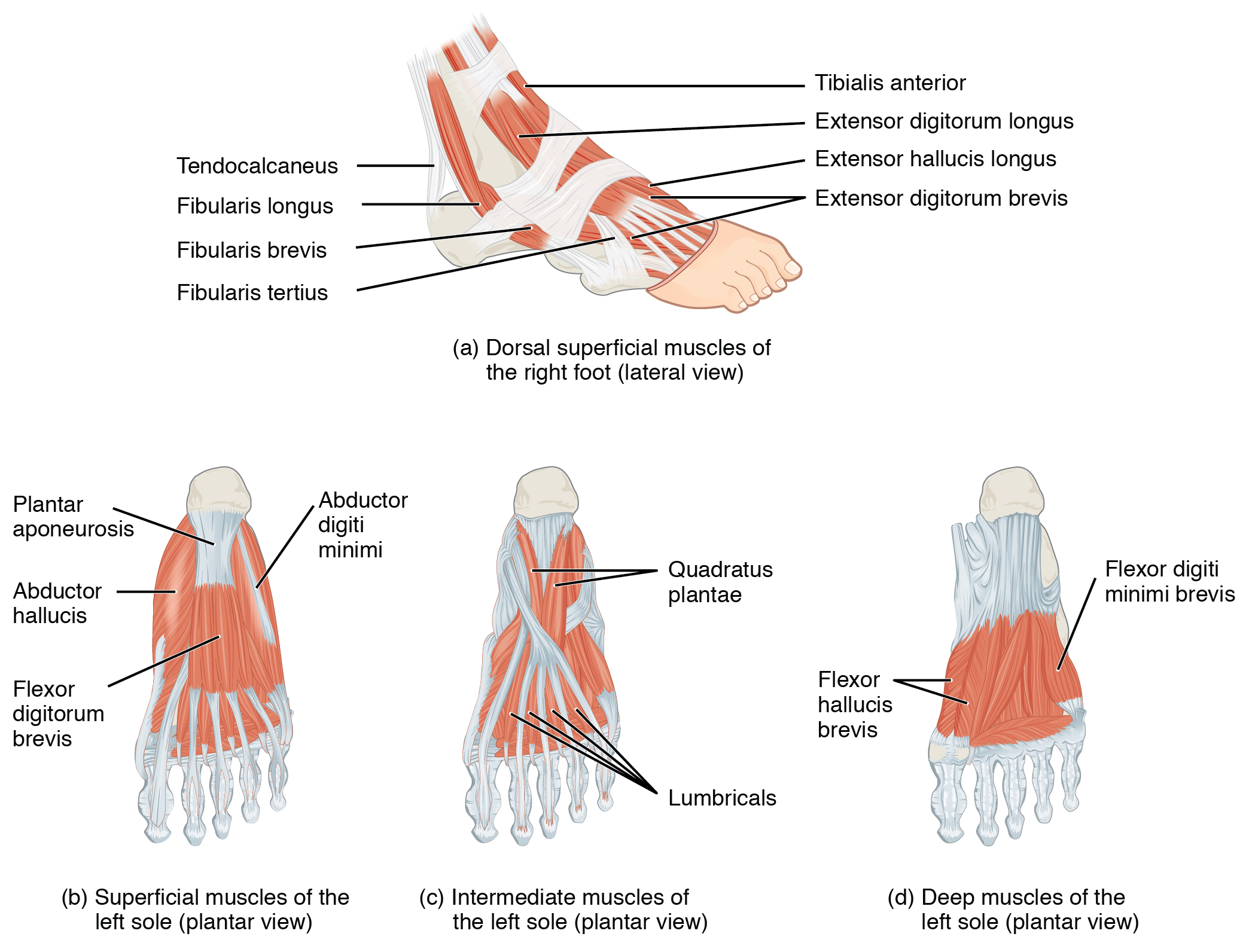
11.6 Appendicular Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs
The toes and feet indicate your head and neck. Massaging your toes in foot reflexology means working your head and neck. The insides of your feet correlate to your spine. The area just underneath your toes corresponds to the chest. The thinnest part of your foot, usually found towards its center, is known as the waistline.

Anatomy Of The Ankle Joint
Bones of foot. The 26 bones of the foot consist of eight distinct types, including the tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges, cuneiforms, talus, navicular, and cuboid bones. The skeletal structure of.

The Anatomy Of The Foot Anatomy Of The Foot Human Anatomy Diagram
When to see a doctor Summary The foot is an intricate part of the body, consisting of 26 bones, 33 joints, 107 ligaments, and 19 muscles. Scientists group the bones of the foot into the.

nerves in bottom of foot Google Search natural healing Pinterest
The hindfoot This is comprised of the talus bone and the calcaneum. The talus connects with the tibia and fibula to form the ankle joint, and the calcaneum is the bone that forms the heel bone (ball of the foot). The calcaneum is the largest bone in the foot. The muscles, tendons and ligaments

Notes on Anatomy and Physiology Using Imagery to Relax the Weight
Metatarsalgia. Metatarsalgia is a condition that causes pain in the ball of the foot. It occurs when the metatarsals, the bones in the foot, become irritated. Metatarsalgia can be caused by overuse, tight muscles, or high heels. Treatment of metatarsalgia often includes icing, stretching, and physical therapy.

Human Foot Anatomy Photograph by Pixologicstudio/science Photo Library
In most two-footed and many four-footed animals, the foot consists of all structures below the ankle joint: heel, arch, digits, and contained bones such as tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges; in mammals that walk on their toes and in hoofed mammals, it includes the terminal parts of one or more digits. The parts of a dog's hind foot and.

feet map of organs in body to read the organ names. It is also
The foot ( pl.: feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate [clarification needed] organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.
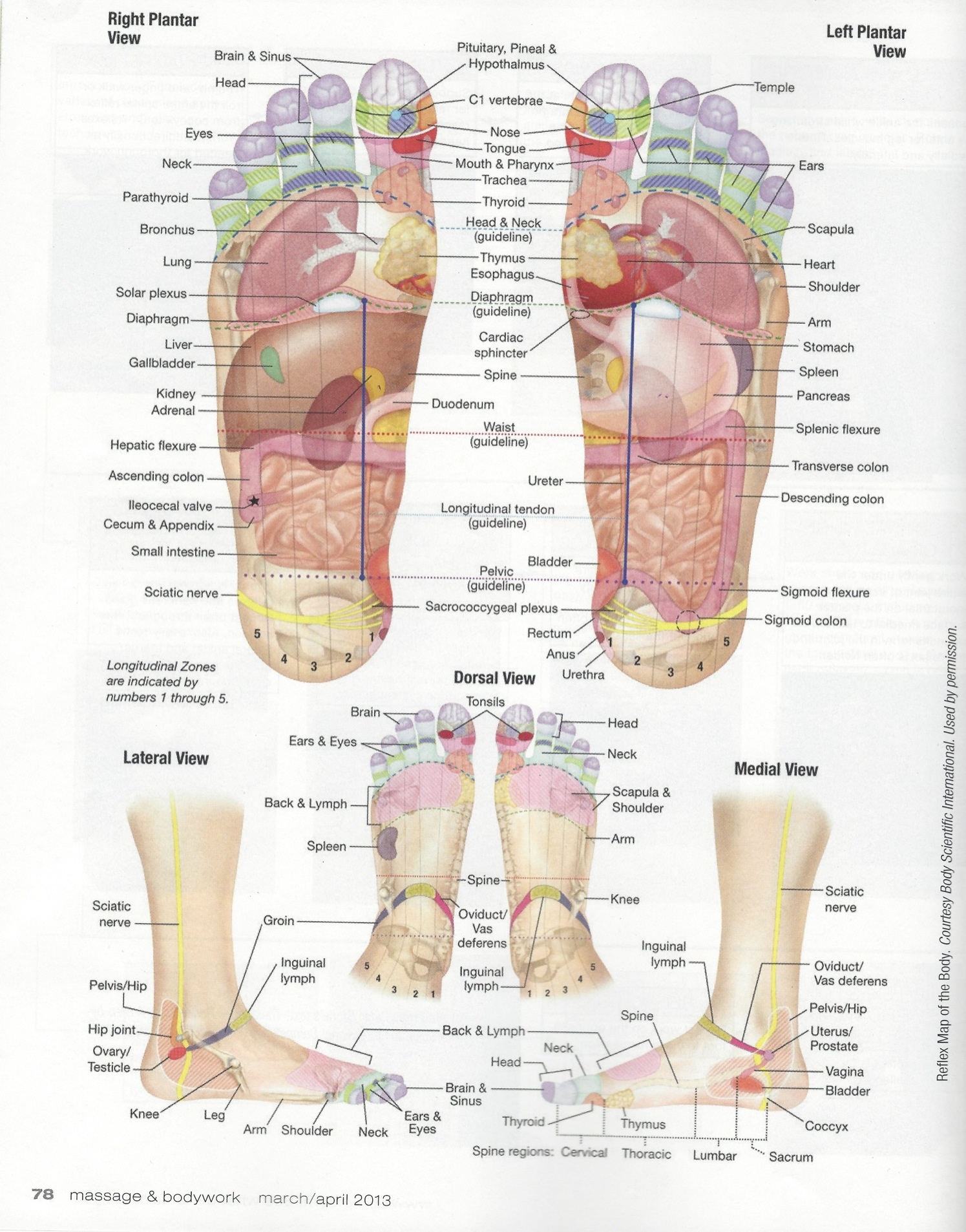
Foot pain relief store, foot pain diagram
The Anatomy of Feet: Bones and Structure. The foot is composed of 26 bones, making up about one-quarter of all the bones in the human body. These bones are divided into three main regions: the hindfoot, midfoot, and forefoot. The hind foot consists of the talus and calcaneus bones, which form the ankle joint and provide stability for weight.

The power of reflexology
LABELED DIAGRAMS. Figure 1. Sections and Bones of the Foot A. Lateral (Left) B. Anterior (Right) Figure 2. Compartments of the Foot A. Cut Section through Mid-Foot. Figure 3. First Layer of the Foot A. Plantar View of Right Foot. Figure 4. Second Layer of the Foot A. Plantar View of Right Foot.